Appearance
Vue3 Reactivity 响应式原理
Vue 和 React 的一大区别,就是响应式数据的区别。
在 React 中,想要触发相关依赖数据和页面的更新,需要手动地去调用 set 函数,通知 React 来进行一个响应式的更新。
而在 Vue 中,只需要修改数据,Vue 就能够自动得追踪数据的变化,自动得对相关依赖数据和页面进行更新。
观前防杠
本文只是对该课程所进行的一个错误的,间接的,庸俗的,主观的,残缺的,平面的,片面的,粗略的,浅显的,简单的有损压缩,总结的一份个人学习笔记。看完文章如对 Vue3 产生了稍微的兴趣和理解和疑问,欢迎大家前去原视频进行观摩学习,课程的最后还有尤雨溪大佬会一起进行一些 QA 和源码的解读。
简单的 Vue
首先我们来看一个简单的 Vue 的基本模版,可以看到当我们对 quantity 进行修改之时,total 能够响应式的变更。
vue
<template>
<div>price: {{ price }}</div>
<div>
quantity:
<input v-model="quantity">
</div>
<div>total: {{ price * quantity }}</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { ref, computed } from 'vue'
const price = ref(5)
const quantity = ref(2)
const total = computed(() => price.value * quantity.value)
console.log({ total })
quantity.value = 5
console.log({ total })
</script>普通的 JavaScript
js
let price = 5
let quantity = 2
let total = price * quantity
console.log({ total })
quantity = 20
console.log({ total })在普通的 js 代码中我们可以看到,total 的值只会停留在第一次定义的时候,并不会跟着 quantity 进行响应式的变化,我们要做的就是让 total 能够根据它的依赖,进行响应式的更新。
如何更新具体的属性
首先为了储存类似 let total = price * quantity 的代码,并之后能重新运行,我们需要
- effect 需要进行操作的函数
- dep 储存众多 effect 依赖
- track 把 effect 添加进依赖
- trigger 调用所有储存的代码
首先我们定义一个 effect 表明 total 的依赖关系,新建一个存储关于 quantity 依赖的集合 dep: Set<Function>,track 用于往 dep 中 添加相关的 effect,等到 quantity 时,通过 trigger 来执行所有依赖 quantity 的 effect。
js
let price = 5
let quantity = 2
let total = price * quantity
let dep = new Set()
let effect = () => { total = price * quantity }
function track () { dep.add(effect) }
function trigger () { dep.forEach(effect => { effect() }) }
track() // save code
effect() // run first
console.log({ total })
quantity = 10
console.log({ total })
trigger() // run all code we saved
console.log({ total })现在我们的 total 能够随着 trigger 的触发进行更新,但是还只实现了有关单个 quantity 依赖的手动更新,所有的关键步骤都得需要手动执行。
多个属性的依赖
对于我们的 total,很明显需要依赖 price 和 quantity 进行更新,我们先将 price 和 quantity 封装成一个 product 对象,它的每个属性都需要自己的 dep: Set<Function>,dep 中的每个值都是我们需要执行的 effect。为了便于管理每个 dep,我们需要一个 depsMap: Map<string, Set<Function>> 来管理响应式对象中所有属性的 dep。
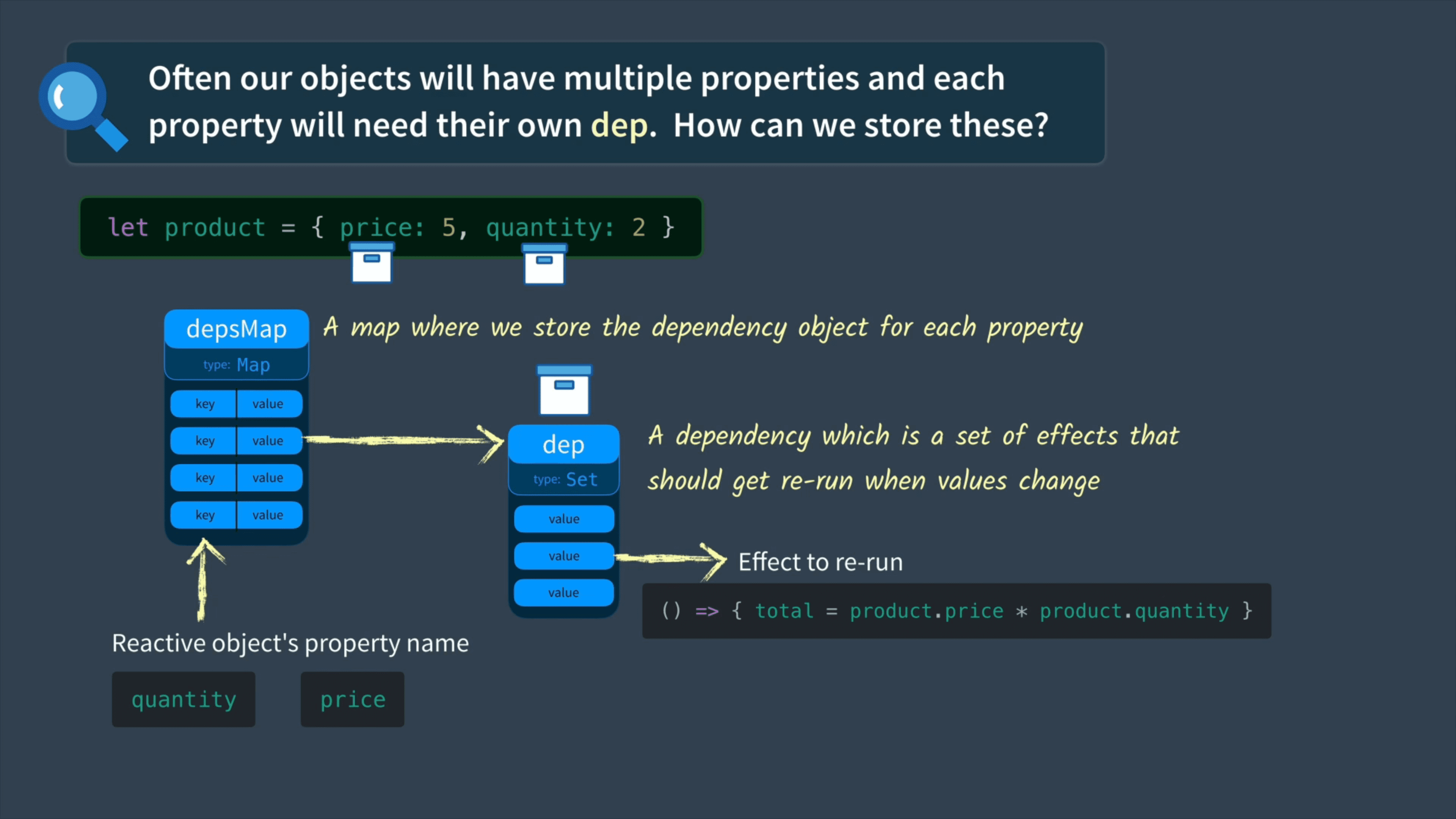
接下来来更新一下代码,为 product 建立一个 depsMap,通过 track 来生成 product 中单个属性的 dep,并往 dep 中存入 effect,在 trigger 阶段,也从 depsMap 中取出指定的 dep,遍历执行相关的 effect。
js
const product = { price: 5, quantity: 2 }
let total = 0
let effect = () => { total = product.price * product.quantity }
const depsMap = new Map()
function track (key) {
if (!depsMap.has(key)) {
depsMap.set(key, new Set)
}
depsMap.get(key).add(effect)
}
function trigger (key) {
const dep = depsMap.get(key)
if (dep) {
dep.forEach(effect => { effect() })
}
}
track('quantity')
effect()
console.log({ total })
product.quantity = 10
trigger('quantity')
console.log({ total })现在我们就能够实现追踪多个属性来手动响应式的更新我们的 total。
多个对象的依赖
当我们不止有一个响应式对象时(product,user),我们还需要一个对象来存储我们每个响应式对象的依赖关系。这里我们用到一个 tatgetMap: WeakMap<object, Map<string, Set<Function>>>
WeakMap对象也是键值对的集合。它的键必须是对象类型,值可以是任意类型。它的键被弱保持,也就是说,当其键所指对象没有其他地方引用的时候,它会被 GC 回收掉。WeakMap提供的接口与Map相同。
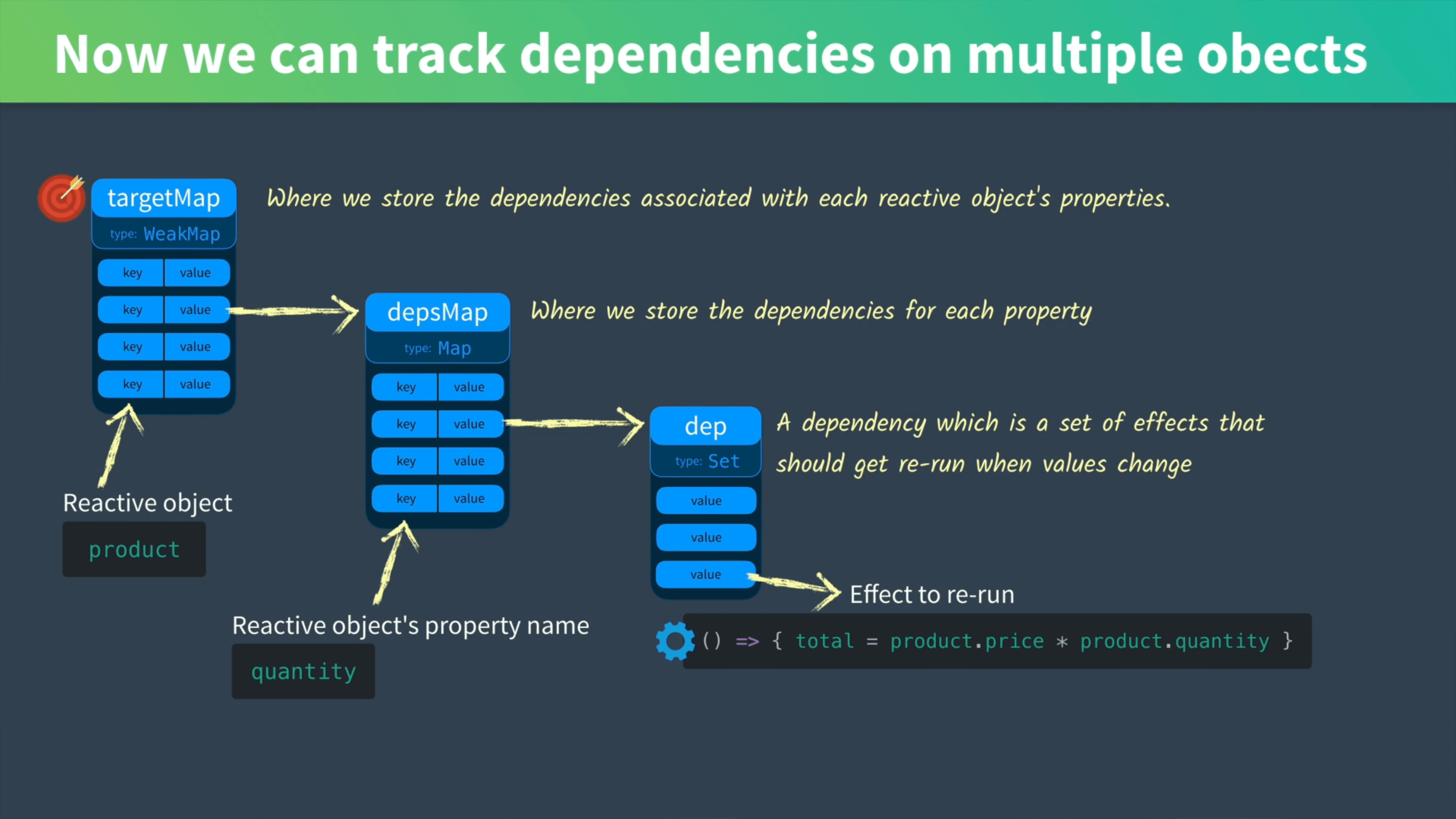
这样,我们就可以直接将整个对象作为我们的 key,存入每个对象的 depsMap 了
js
const targetMap = new WeakMap()
function track (target, key) {
if (!targetMap.has(target)) {
targetMap.set(target, new Map())
}
const depsMap = targetMap.get(target)
if (!depsMap.has(key)) {
depsMap.set(key, new Set)
}
depsMap.get(key).add(effect)
}
function trigger (target, key) {
const depsMap = targetMap.get(target)
if (!depsMap) {
return
}
const dep = depsMap.get(key)
if (dep) {
dep.forEach(effect => { effect() })
}
}
track(product, 'quantity')
effect()
console.log({ total })
product.quantity = 5
trigger(product, 'quantity')
console.log({ total })现在我们就有地方可以存下每个对象的每个属性的相关依赖,有 track 和 trigger 来存入和调用每个对象的每个属性的依赖的 effect,接下来我们要做的,就是要响应式地调用 track 和 trigger。
响应式
大家有准备过面试题的话,应该都有看到过 Vue2 使用的是 es5 的 Object.defineProperty 来实现响应式,而 Vue3 使用 es6 的 Proxy 和 Reflect 来优化 Vue2 中的诸多问题,也顺便放弃了对 ie 浏览器的支持。
proxy
Proxy,顾名思义就是对原对象进行的一层代理,在 proxy 中实现基本操作的拦截和自定义。
Reflect,简单来说就是能够通过传入的 receiver,来实现 this 的正确指向。
js
const product = { price: 5, quantity: 2 }
const proxiedProduct = new Proxy(product, {
get (target, key, receiver) {
// ...
console.log('get')
return Reflect.get(target, key, receiver)
},
set (target, key, value, receiver) {
// ...
console.log('set')
return Reflect.set(target, key, value, receiver)
}
})
proxiedProduct.quantity = 99
console.log(proxiedProduct.quantity)响应式的 track 和 trigger
有了 proxy,我们就可以实现一个 Vue3 上的 reactive 函数,在 reactive 函数中实现响应式,在 proxy 的 get 和 set 中调用 track 和 trigger。
js
function reactive (target) {
const handler = {
get (target, key, receiver) {
track(target, key)
return Reflect.get(target, key, receiver)
},
set (target, key, value, receiver) {
const oldValue = target[key]
const result = Reflect.set(target, key, value, receiver)
if (oldValue !== value) {
// trigger 要在 set 之后,不然 effect 里拿到值还是老的。。
trigger(target, key)
}
return result
}
}
return new Proxy(target, handler)
}
const product = reactive({ price: 5, quantity: 2 })
let total = 0
let effect = () => { total = product.price * product.quantity }
effect()
console.log({ total })
product.quantity = 5
console.log({ total })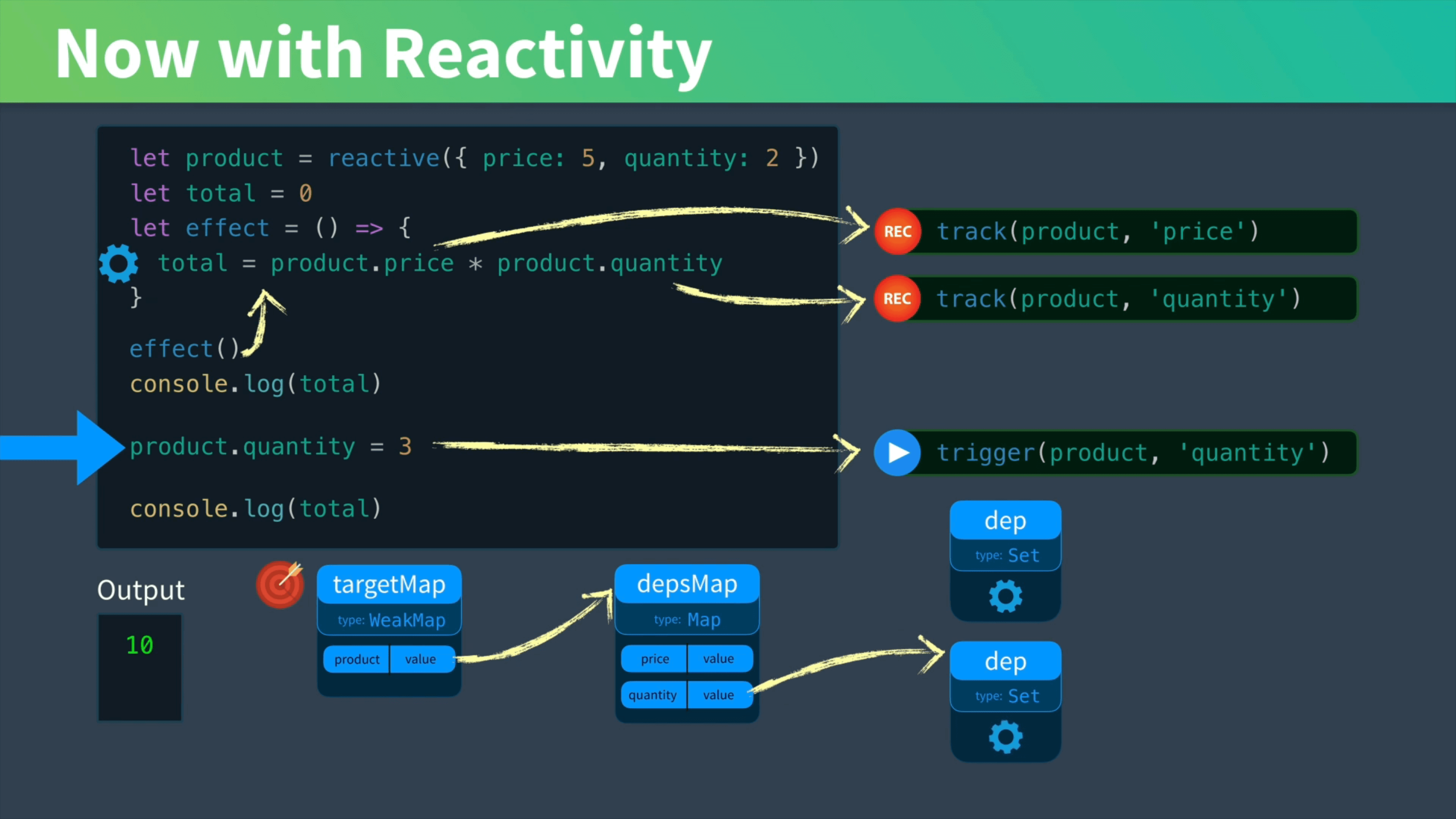
现在,我们成功的实现了 total 的响应式更新,当然还是有缺陷,对于 effect,我们还只是使用了一个全局的 effect,如果有了多个属性需要响应式更新,每个 dep 所存储的都是这唯一的 effect;对于 track,也可以发现每次 get 都会重复的调用 track,虽然 targetMap 中的 depsMap 中的 dep 是个 Set,不会重复存入同一个 effect,但还是有空间可以再优化一下。
优化 track & effect
为了优化 track 过多的调用,并解耦 effect,我们将 effect 提升为一个全局函数。
js
let activeEffect = null
function effect (fn) {
activeEffect = fn
activeEffect()
activeEffect = null
}
const targetMap = new WeakMap()
function track (target, key) {
if (!activeEffect) {
return
}
console.log('track')
if (!targetMap.has(target)) {
targetMap.set(target, new Map())
}
const depsMap = targetMap.get(target)
if (!depsMap.has(key)) {
depsMap.set(key, new Set)
}
depsMap.get(key).add(activeEffect)
}
effect(() => {
total = product.quantity * product.price
})更新测试用例
我们新增一个 salePrice 变量,并且给 salePrice 增加对应的 effect
js
const product = reactive({ price: 5, quantity: 2 })
let salePrice = 0
let total = 0
effect(() => {
total = product.quantity * salePrice
})
effect(() => {
salePrice = product.price * .8
})
console.log({ total, salePrice })
product.quantity = 5
console.log({ total, salePrice })
product.price = 10
console.log({ total, salePrice })当我们修改了 price 时,salesPrice 成功的触发了响应式更新,total 却没有更新,这是当然的,因为我们的 salePrice 只是个普通的变量,并没有响应的 track 和 trigger 可以触发。如何使一个普通变量能够拥有响应式,当然 Vue3 里也提供了这样的功能。
ref

Vue3 里为基本类型提供了 ref() 这一方法来实现响应式
关于 ref 的实现,我们当然可以通过简单的套壳 reactive。
js
function ref (value) {
return reactive({ value })
}但在 Vue3 中,ref 是通过 es5 中的对象访问器 getter 和 setter 来实现的。
js
function ref (raw) {
const result = {
get value () {
track(result, 'value')
return raw
},
set value (newVal) {
if (raw !== newVal) {
raw = newVal
trigger(result, 'value')
}
}
}
return result
}
const product = reactive({ price: 5, quantity: 2 })
let salePrice = ref(0)
let total = 0
effect(() => {
total = product.quantity * salePrice.value
})
effect(() => {
salePrice.value = product.price * .8
})
console.log({ total, salePrice: salePrice.value })
product.quantity = 5
console.log({ total, salePrice: salePrice.value })
product.price = 10
console.log({ total, salePrice: salePrice.value })computed
computed 函数也是 Vue 中提供的响应式工具
接受一个 getter 函数,返回一个只读的响应式 ref 对象。该 ref 通过 .value 暴露 getter 函数的返回值。它也可以接受一个带有 get 和 set 函数的对象来创建一个可写的 ref 对象。
js
function computed (getter) {
const result = ref()
effect(() => { result.value = getter() })
return result
}
const product = reactive({ price: 5, quantity: 2 })
let salePrice = computed(() => { return product.price * .8 })
let total = computed(() => { return product.quantity * salePrice.value })
console.log({ total: total.value, salePrice: salePrice.value })
product.quantity = 5
console.log({ total: total.value, salePrice: salePrice.value })
product.price = 10
console.log({ total: total.value, salePrice: salePrice.value })看看 Vue3 源代码
在 GitHub 上,我们可以在 packages/reactivity/src 的文件夹里看到这些文件,对应了我们上文完成的一些函数和功能。当然和我们的小 demo 比起来,源码里丰富和完善了许多的功能,包括完整的 ts 支持,尽可能全面的边界条件处理等等。
effect.ts
包含了我们小 demo 里的 effect,track,trigger 以及更多
baseHandlers.ts
包含了 proxy 的 get 和 set
baseHandlers 里,个人觉得有意思的就是这个 createArrayInstrumentations 数组 case。
js
const obj = { name: 'hct' }
const arr = reactive([obj])
const reactiveObj = arr[0]
console.log(obj, reactiveObj)
obj === reactiveObj // ??
arr.includes(obj) // ??当我们把一个 obj 放入 reactive 过的数组中再取出来,得到的就是经过 proxy 包裹的响应式对象。

那么当我们对响应式数组使用数组的方法时传入的普通对象和 proxy 对象也得进行一层处理才能返回符合常识的结果。
reactive.ts
proxy 的响应式可以做到懒加载,Vue2 的 Object.defineProperty 就必须立即转化 depend。
proxy 对于新增的属性能够做到自动追踪,defineProperty 就只能另外通过 Vue.set(key, value) 来实现。
ref.ts
为什么不直接用 reactive,只暴露 value,不想让使用者手动往 ref 里加东西。
computed.ts
结尾引流
通过本文,希望大家能够对 Vue3 的响应式原理产生或多或少一定的了解,如果有兴趣,各位还能继续通过《跟尤雨溪一起解读Vue3源码》课程,继续和尤大一起完成一个简单的 vue(还能看到尤大手写代码时,写出低级错误后当场 debug 的有趣名场面 😆),欢迎大家去点赞投币收藏一键三连。
